Neurons and Synapses
Neurons and Synapses: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Neurons, Synapse, Neurotransmitters, Action Potential, Sodium-Potassium Pump, Myelin Sheath, Nerve Impulse, Myelinated Nerve Fiber, Resting Potential, Neonicotinoids and, Non-myelinated Nerve Fiber
Important Questions on Neurons and Synapses
What are myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibres?
What causes depolarization of a nerve?
Observe the given graph showing the phases of action potential and name the part labelled as X.
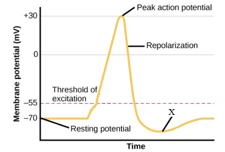
Describe hyperpolarization of a neuronal membrane.
Describe action potential of a neural membrane.
An oscilloscope shows time on the X axis and membrane potential on the Y axis.
Describe neonicotinoids and their use.
Neonicotinoids are banned by European countries as they are linked to bee decline.
In the resting state of the neural membrane, diffusion due to concentration gradients, if allowed would drive
Rank the following as cell, tissues, organ or organism-
Neuron
Give a reason for following.
Nerve cells are long and branched.
During synaptic transmission of nerve impulses, the neurotransmitter is released from synaptic vesicles by the action of ions. Choose the correct and .
What is Myelin? How are myelinated neurons different from unmyelinated neurons?
Write 'true' or 'false'.write the correct statement.
Myelinated axons transmit impulses faster than unmyelinated axons.
Chemical transmission in synapse occurs due to
The potential difference between outside and inside of a nerve before excitation is known as action potential.
Excitation of neurons occurs when the external stimuli changes their
The chemical substance released by parasympathetic nervous system is
Write name of a neurotransmitter?
